
To determine the relative atomic mass for an element we need to:.The relative atomic mass is determined by assigning the relative isotopic mass of carbon –12 as 12 and finding the relative abundance of each isotope of that element.
It is relatively easy to isolate and purify this isotope.The element Carbon 12 was chosen as a reference since: The advantage of a relative scale is that very large or very small numbers can be compared relatively easy. = 6 x 1.67 x 10^-24 + 6 x 1.67 x 10^-24 + 6 x 9.11 x 10^-28 gĪ relative scale is one in which all measurements are compared to one standard or reference measure. Most elements have 2 or more naturally occurring isotopes.Įxample: Carbon has 3 isotopes.Isotopes of an element have the same atomic number (number of protons) but a different mass number (number of protons and neutrons).They have the same chemical properties as they all have same number of valence electrons which is 4 but different physical properties since their mass numbers are different. Understand that isotopes have the same properties because they have the same number of electrons in their outer shell.Įxample: carbon- 12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are isotopes of carbon as they have same proton number of 6.Industrial use: in tracers such as Geiger counter to check oil and gas pipes for leaks Medical uses: Cobalt-60 used in radiotherapy to cure cancer, Cobalt-60 and cesium-137 used to sterilise syringes and other disposable medical equipment. State one medical and one industrial use of radioactive isotopes.The atom breaks down naturally or decays, giving out radiation in the form of rays and particles and large amount of energy. State the two types of isotopes as being radioactive and non-radioactive.Įxample: Carbon -14 is radioactive, its nucleus is unstable.But carbon- 12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 have 6 neutrons, 7 neutrons and 8 neutrons respectively. Define isotopes: atoms of the same element which have the same proton number but a different nucleon numberĮxample: carbon- 12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are isotopes of carbon as they have same proton number of 6.Noble gases (Group VIII) have fully filled electron shells and stable electronic configuration so they do not need to gain or lose electrons thus noble gases are inert and unreactive. Sulfur atom also has 3 electron shells.Įlements in the periodic table are arranged in increasing proton number.Ītoms of Elements in same group (vertical column) have same number of valence electrons and similar chemical properties.Ītoms of elements in the same period (horizontal row) have same number of electron shells. The last number of the electronic configuration will show the valence/outermost electrons of the atom.
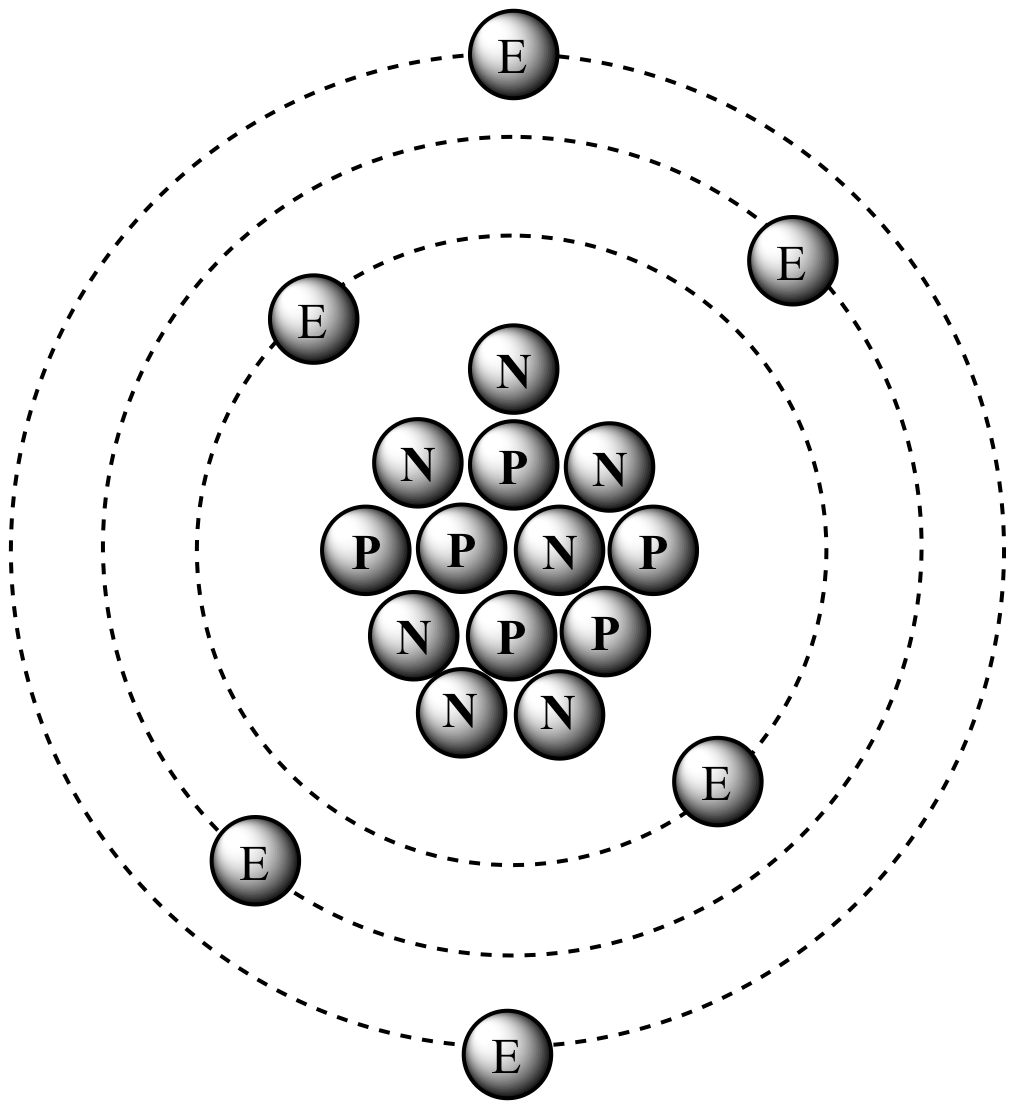
The numbers are separated by ‘dot’.Įlectronic configuration of sulfur atom will be 2.8.6 as it has 16 electrons. Lastly remember to write the symbol of the atom in the middle of the atom.Įlectronic structure of sulfur atom with 16 electrons will look like this:Įlectronic configuration shows distribution of electrons of an atom in electron shells without drawing.įirst number stands for number of electrons in first shell, and second number, third and fourth number shows for number of electrons in second, third and fourth shell respectively. Third electron shell hold maximum 8 electrons (Not true for A levels, IB syllabus). Second electron shell hold maximum 8 electrons.
#Carbon 14 atomic number how to#
How to draw electronic structure of atom:įirst electron shell holds maximum 2 electrons.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
